Examelot
Examelot
Report a problem
The ASCP Phlebotomy Technician (PBT) certification exam assesses the knowledge required for entry-level phlebotomy positions. The American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) administers the exam.
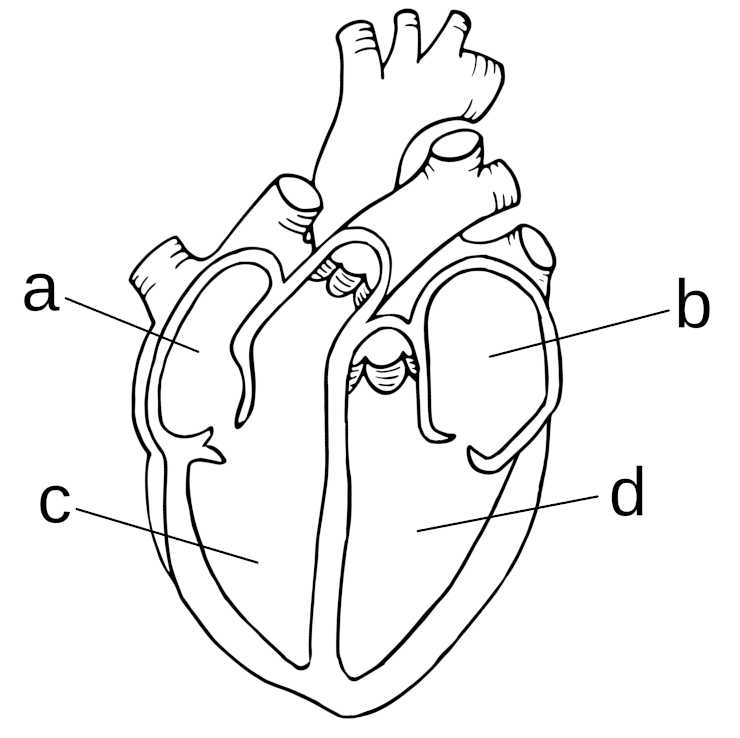
The exam consists of 100 multiple-choice questions and has a 2 hour time limit. Exam topics include specimen collection, processing, and transport; waived testing; point-of-care testing; laboratory procedures; non-blood specimens (urine, sputum, swabs, etc.); the circulatory system; and patient interaction.
The exam fee is $145.
These practice questions will help prepare you for the ASCP PBT exam.
This page contains 400 practice questions divided into the six sections of the exam: 1. Circulatory system, 2. Specimen collection, 3. Specimen handling, transport, and processing, 4. Waived and point-of-care-testing, 5. Non-blood specimens, and 6. Laboratory operations.
All questions have been carefully designed to mimic the questions on the real exam, to help you prepare and get a passing grade.